Designing resilient apps in 2020
⏱ Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Table of Contents
By Mickaël Andrieu, Software architect & Instructor
The recent history of PrestaShop
PrestaShop was the e-commerce leader in 2019 with the following statistics:
- 300k online shops;
- 30% market share in France;
- 65 supported countries.
PrestaShop’s back-office contains modules that may retrieve a lot of information server-side from many third-party services. These services include but are not limited to analytics, ads, tips and tricks, updates, news. What happens if one of these services were to become available?
By the end of 2017, shop administrators started complaining about their back-office slow response times. The Core team could indeed reproduce the issue and trace its source to a third-party service that went down and caused timeouts when called. Unfortunately, such issues go far beyond just back-offices as it caused a loss of trust, brand perception and therefore money. Not only that but updates could not be installed without the consent of the site administrators that could not access their back-office.
Resilience
Resilience is the capacity of a system to resist a degradation of its ecosystem. Improving resilience is an effort that must come both from the infrastructure and from the software side of the stack:
- Use managed infrastructure;
- Rely on a CDN;
- Load balance your applications;
- Play on Service Level Agreements or SLAs:
- 99% (Two 9s) is 3.65 days of unavailability per year;
- 99.9% (Three 9s) is 8.76 hours of unavailability per year;
- 99.99% (Four 9s) is 52.56 minutes of unavailability per year;
- 99.999% (Five 9s) is 5.26 minutes of unavailability per year;
- 99.9999% (Six 9s) is 31.54 seconds of unavailability per year;
- The more 9s, the stable the service but also the more expensive with a factor of about ten per 9;
- Durability is the guarantee that data is preserved while availability means the service operates normally. This should be considered when developing sensitive services, especially in a legal context.
- Improve code quality: Cloud providers are not the only ones responsible for your service downtime. Your team should guarantee the best experience.
For instance, for the code quality improvement it is possible to use timeouts for HTTP requests, make the package non-blocking or asynchronous and prepare fallbacks in case something goes wrong. If you configure a timeout server-side, make sure it is shorter than your maximum execution time, otherwise it is rendered useless. In addition, do not return generic errors; null, undefined and empty or meaningless strings will not add information in the event of a timeout.
Circuit Breaker
The Circuit Breaker pattern relies on the notion of protocols and social contracts. You knock on a door, no one answers, you might knock again, then a third time, etc. The way you knock, your process, all of this is part of your social contract and in turn of your own Circuit Breaker.
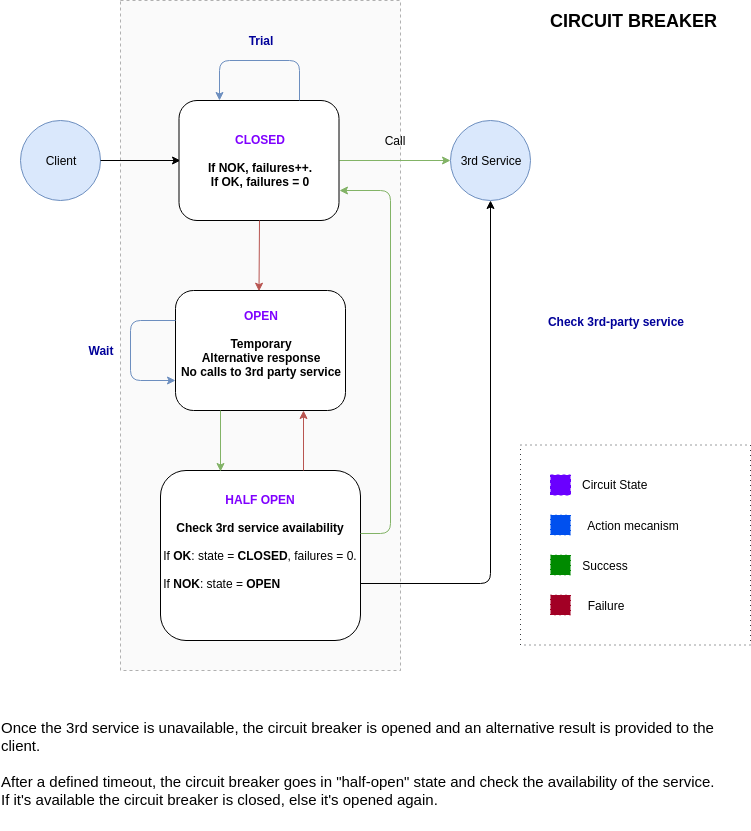
How a Circuit Breaker works, credits: PrestaShop/circuit-breaker
In the best scenario, the circuit is said to be closed and the covered system to be open. When facing unavailability, the circuit applies a degraded behavior. Is is then said to be open and the covered system to be closed or isolated. The capacity to reach the closed or isolated system is degraded until its recovery.
The circuit reopens itself temporarily after a while. Depending on the response of the once isolated system, it will stay open or close itself again. Circuit Breaker implements the Retry and the Timeout patterns and can present a degraded mode to the requester.
In PHP
By the end of 2017, only one library implemented the Circuit Breaker pattern: Ganesha. However, its architecture was not satisfactory enough. This led to the implementation of PrestaShop/circuit-breaker, now in use in more than 150k websites!
Resiliency is another implementation derived from
circuit-breaker. Refreshed, more promising and easy to install: composer require love-oss/resiliency.
Resiliency operates around four major components:
- An HTTP client: Guzzle by default;
- A persistent storage for the Circuit Breaker state;
- A configuration object for values such as timeouts;
- An event dispatcher to add behaviors.
The event dispatcher in Resiliency is the one from Symfony. It exposes the events “Initiated”, “Tried”, “Opened”, “ReOpened”, “Closed”, “AvailabilityChecked” / “HalfOpened”, “Reseted” and “Isolated”. “Reseted” and “Isolated” are manual overrides mapping to closing the circuit or opening it. These events allow implementing additional features such as logging, interceptors, etc.
The chosen HTTP client must handle HTTP as well as HTTPS and support timeouts. Resiliency is compatible with Guzzle 6, Guzzle 7 and Symfony HTTP Client.
PHP processes die after the end of each request but the Circuit Breaker pattern requires remembering a state. To that end, Resiliency supports in-memory persistence that can be used in tests or with an async PHP installation, files, Doctrine ORM, Memcached, Redis, etc. This is rendered possible thanks to the usage of the Symfony Cache component.
Testing
Testing resilience seems complex. Fortunately, there are test HTTP clients that can mock responses. This leaves verification of the state of the circuit breaker and the response content to the test. To avoid testing from outside, it is recommended to use the event system. Testing unavailability is simpler than testing slowness in PHP today.
Questions and Answers
Does the circuit breaker only opens on timeouts?
It is possible to open it when catching an exception but this is not default behavior.
Should the degraded timeout be slower or faster?
It could be interesting to place a shorter degraded timeout to prove the service stability before closing the circuit breaker. This setting depends on the preferences of the development team.
Is Resiliency domain-based or URL-based?
It is URL-based and creates a different circuit breaker per URL, excluding resource IDs.
Is it possible to generalize Resiliency to any external call instead of just HTTP?
There is a good example about that in C#: Polly. By the way, Resiliency takes inspiration from that library, notably its event system, Isolation and Reset behaviors.
Is Resiliency still maintained?
No, however it is stable. The current v1 is final as it solves a simple problem in a simple manner. A v2 is planned somewhere in the future. Maintainers are welcome!